Rigid PCBs Demystified: Understanding the Basics
Unveiling the Secrets: A Comprehensive Guide to Rigid Printed Circuit Boards
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronic devices, enabling the seamless integration of various components. Among the different types of PCBs, rigid PCBs play a crucial role in providing stability and durability. This article aims to demystify the basics of rigid PCBs, unveiling their construction, design considerations, manufacturing processes, and applications.
1. What is a Rigid PCB?
A rigid PCB is a type of printed circuit board that is manufactured using a solid, inflexible substrate material. It provides mechanical support and electrical connectivity between electronic components. Rigid PCBs are composed of multiple layers of conductive copper traces and insulating materials, typically FR-4, which is a flame-retardant epoxy-based material.
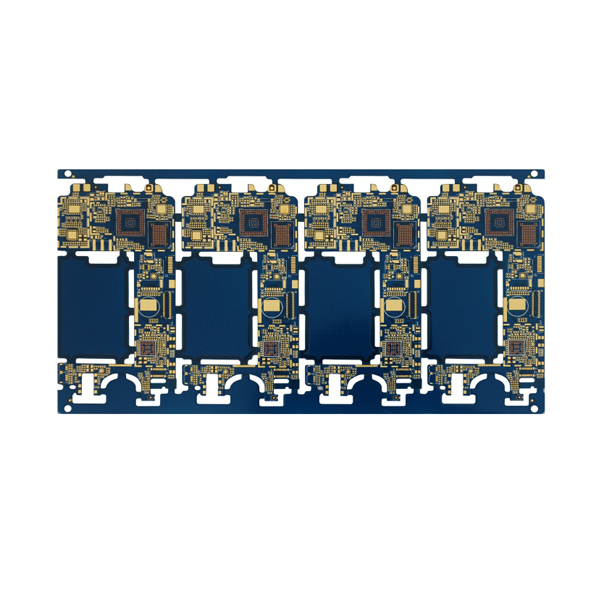
2. Construction and Design Considerations
The construction of a rigid PCB involves several key components and design considerations. These include:
a) Substrate Material: The choice of substrate material depends on factors such as cost, performance, and application requirements. FR-4 is the most commonly used material due to its excellent electrical insulation and mechanical properties.
b) Copper Layers: Rigid PCBs consist of multiple layers of conductive copper traces, which are etched to create the desired circuit pattern. The thickness of copper layers affects the board's electrical performance and heat dissipation capabilities.
c) Vias: Vias are essential components that establish electrical connections between different layers of a rigid PCB. They enable the flow of signals and power between various components and ensure the integrity of the circuit.
d) Component Placement: Proper component placement is crucial for optimizing circuit performance, minimizing signal interference, and facilitating efficient manufacturing processes. Factors such as component size, heat dissipation, and signal integrity need to be considered during the placement process.
3. Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of rigid PCBs involves several sequential processes:
a) Design and Layout: The design and layout phase involves the creation of a schematic diagram and the placement of components on the PCB. This step ensures the optimal arrangement of traces, vias, and components for efficient operation.
b) Photolithography: Photolithography is used to transfer the PCB design onto the copper layers. It involves the application of a photoresist material, exposure to ultraviolet light, and subsequent etching to remove unwanted copper, leaving behind the desired circuit pattern.
c) Drilling and Plating: After the circuit pattern is formed, the PCB undergoes drilling to create holes for component mounting and vias. These holes are then plated with copper to ensure electrical conductivity between layers.
d) Solder Mask and Silk Screen Printing: A solder mask is applied to the PCB to protect the copper traces and prevent short circuits. Silk screen printing is used to add component labels, logos, and other identifying information.
e) Testing and Inspection: Rigorous testing and inspection are performed to ensure the functionality and quality of the manufactured PCB. Electrical testing, visual inspection, and automated optical inspection (AOI) are commonly employed techniques.
4. Applications of Rigid PCBs
Rigid PCBs find applications in a wide range of industries, including:
a) Consumer Electronics: Rigid PCBs are extensively used in smartphones, tablets, laptops, televisions, and other consumer electronic devices due to their compact size and high reliability.
b) Automotive: Rigid PCBs are crucial components in automotive electronics, facilitating various functions such as engine control, infotainment systems, safety features, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
c) Industrial Automation: Rigid PCBs play a significant role in industrial automation applications, including control systems, robotics, process monitoring, and data acquisition.
d) Medical Devices: Medical devices such as MRI machines, pacemakers, and diagnostic equipment rely on rigid PCBs for precise and reliable operation.
5. Conclusion
Rigid PCBs are the backbone of modern electronics, providing stability, reliability, and electrical connectivity. Understanding the basics of rigid PCB construction, design considerations, manufacturing processes, and applications is essential for engineers, designers, and manufacturers in the electronics industry. By demystifying rigid PCBs, this article aims to equip readers with the knowledge needed to harness the potential of this fundamental technology.
Send PCB Files to Sales@ucreatepcba.com, We Will Quote You Very Soon!
Request PCB Manufacturing & Assemble Quote Now



